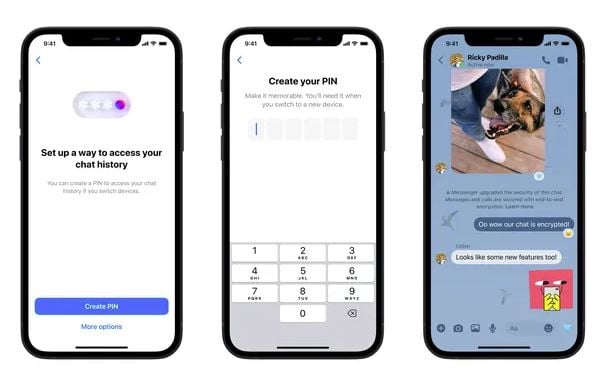
After virtually 5 years of labor, which has included varied regulatory challenges, Meta has lastly moved to the subsequent stage of its roll-out of end-to-end (E2E) encryption because the default in Messenger.
The replace, Meta says, has required a ground-up re-build of the app, with stronger privateness on the core, which can present extra assurance to customers that their non-public chats will stay that approach, irrespective of who may search to infiltrate them, be it Meta or anyone else.
As defined by Meta:
“The additional layer of safety supplied by end-to-end encryption signifies that the content material of your messages and calls with family and friends are protected against the second they depart your gadget to the second they attain the receiver’s gadget. Which means that no one, together with Meta, can see what’s despatched or mentioned, until you select to report a message to us.”
The shift to full encryption by default strikes Messenger extra into line with WhatsApp, and was initially introduced as a part of Meta’s broader plan to combine its varied messaging instruments, so as to simplify cross-app communication. That, conceptually, will finally additionally see the event of a single, common inbox that may embody your entire Messenger, WhatsApp, and IG Direct chats, and will probably be accessible from every service.
That plan did appear to have hit a slight snag not too long ago, with Meta saying that it’s eradicating the choice to conduct cross-app chats between Fb and Instagram, although that replace might even have been made in preparation for this transformation, with IG Direct chats nonetheless not encrypted by default.
Or it could possibly be associated to new E.U. rules, and Meta’s effort to align Messenger and Instagram Direct with Fb and IG, so as to keep away from them being ruled individually (I requested Meta for readability on the reasoning, however bought no response).
Both approach, your entire Messenger chats will quickly be encrypted, whereas Meta’s additionally including another new options to carry Messenger additional into line with WhatsApp’s capabilities.
First off, you’ll quickly be capable of edit your messages for as much as quarter-hour after you ship them, the identical as you’ll be able to on WhatsApp.

Disappearing messages can even final for twenty-four hours, as they do on WhatsApp, whereas Meta’s additionally making it simpler to see when disappearing messages are lively in your chats.

Meta’s additionally added new learn receipt controls, and improved visible show choices, together with variable playback speeds for audio messages. Once more, like WhatsApp.
However encryption is the large addition, and the one which Meta has been combating to enact, regardless of varied teams opposing the change, because of the danger that it might facilitate extra felony exercise in Meta’s apps.
The U.Okay. Authorities has been one of many strongest opponents, with former U.Okay. Residence Affairs Secretary Priti Patel repeatedly calling on Meta to rethink its plans for expanded messaging encryption, because of the potential limitation that it might impose on police making an attempt to analyze and stop youngster abuse. In September final 12 months, Patel labeled the shift to full encryption as ‘catastrophic’.
Varied different safety officers have voiced related considerations, and it stays a key concern inside this shift.
The counter, then, is the potential for governments and/or company homeowners to eavesdrop on folks’s non-public messages if encryption isn’t enabled.
As Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg outlined again in 2021:
“There’s a rising consciousness that the extra entities which have entry to your information, the extra vulnerabilities there are for somebody to misuse it or for a cyber assault to reveal it. There may be additionally a rising concern amongst some that know-how could also be centralizing energy within the fingers of governments and corporations like ours. And a few folks fear that our companies might entry their messages and use them for promoting or in different methods they do not anticipate.”
Nevertheless it goes additional than that, particularly when contemplating folks dwelling below authoritarian regimes, or in warfare zones, the place with the ability to share info anonymously might truly be important to somebody’s survival.
“Within the final 12 months, I’ve spoken with dissidents who’ve informed me encryption is the rationale they’re free, and even alive. Governments usually make illegal calls for for information, and whereas we push again and combat these requests in courtroom, there’s all the time a danger we’ll lose a case – and if the knowledge is not encrypted we might both have to show over the info or danger our staff being arrested if we didn’t comply.”
WhatsApp chief Will Cathcart has additionally been a powerful proponent for expanded messaging encryption, calling it “one of the crucial highly effective applied sciences we now have to maintain everybody secure”.
So there’s a clear case for encryption, although Meta additionally acknowledges the danger, in facilitating nefarious exercise in its apps, which is already occurring with out encryption.
Earlier this week, The Wall Avenue Journal revealed a report that defined how two unbiased analysis teams, The Stanford Web Observatory and The Canadian Centre for Baby Safety, have each been monitoring varied situations of teams, some with hundreds of thousands of members, which were distributing youngster sexual abuse materials (CSAM) throughout each Fb and Instagram.
And that’s solely what they’ll monitor, with encrypted messaging teams on WhatsApp seemingly additionally facilitating the distribution of CSAM as nicely.
Certainly, all through 2021, Meta detected and reported 22 million items of kid abuse imagery to the Nationwide Centre for Lacking and Exploited Youngsters (NCMEC), whereas in 2020, NCMEC additionally reported that Facebook was liable for 94% of the 69 million youngster intercourse abuse photographs reported by U.S. know-how firms.
Meta is working to deal with this, and it’s consistently eradicating profiles, teams, and posts. However the sheer scale of Meta’s community makes this a unending process, and you’ll solely think about that hiding much more of that from any potential view will worsen the scenario.
Which is why the shift in direction of higher encryption has confronted such scrutiny, and a part of the rationale why it’s taken Meta 5 years to implement.
So is it a very good transfer? I don’t know, nobody does, however there are robust advocates on either side, and clearly, Meta itself is extra aligned with the view that the overwhelming majority of customers solely intend to make the most of stronger safety for good, versus felony function.
However then once more, extra encryption additionally advantages Meta in lots of respects.
In case you can’t detect such exercise, you’ll be able to’t maintain Meta to account for facilitating it, so the extra of it that will get hidden, the much less Meta can probably be held to account for a similar.
Which is why I do have some bother agreeing with Meta’s perspective, however once more, there are numerous unbiased specialists who additionally agree that encryption needs to be the default, and once more, there are lots of different the explanation why it is a constructive transfer.
However there are dangers, and vital ones at that.
Hopefully, the positives do find yourself outweighing such considerations.