Researchers uncover information leaks in Google Tag Supervisor (GTM) in addition to safety vulnerabilities, arbitrary script injections and situations of consent for information assortment enabled by default. A authorized evaluation identifies potential violations of EU information safety regulation.
There are a lot of troubling revelations together with that server-side GTM “obstructs compliance auditing endeavors from regulators, information safety officers, and researchers…”
GTM, developed by Google in 2012 to help publishers in implementing third-party JavaScript scripts, is at present used on as many as 28 million web sites. The analysis research evaluates each variations of GTM, the Shopper-side and the newer Server-side GTM that was launched in 2020.
The evaluation, undertaken by researchers and authorized consultants, revealed various points inherent to the GTM structure.
An examination of 78 Shopper-side Tags, 8 Server-side Tags, and two Consent Administration Platforms (CMPs), revealed hidden information leaks, situations of Tags bypassing GTM permission techniques to be able to inject scripts, and consent set to enabled by default with none consumer interplay.
A big discovering pertains to the Server-side GTM. Server-side GTM works by loading and executing tags on a distant server, which creates the notion of the absence of third events on the web site.
Nonetheless, the research confirmed that this structure permits tags operating on the server to clandestinely share customers’ information with third events, circumventing browser restrictions and safety measures like just like the Content material-Safety-Coverage (CSP).
Methodology Used In Analysis On GTM Information Leaks
The researchers are from Centre Inria de l’Université, Centre Inria d’Université Côte d’Azur, Centre Inria de l’Université, and Utrecht College.
The methodology utilized by the researchers was to purchase a site and set up GTM on a stay web site.
The analysis paper explains intimately:
“To conduct experiments and arrange the GTM infrastructure, we purchased a site – we name it instance.com right here – and created a public web site containing one fundamental webpage with a paragraph of textual content and an HTML login type. Now we have included a login type since Senol et al. …have just lately discovered that consumer enter is usually leaked from the varieties, so we determined to check whether or not Tags could also be accountable for such leakage.
The web site and the Server-side GTM infrastructure have been hosted on a digital machine we rented on the Microsoft Azure cloud computing platform situated in a knowledge heart within the EU.
…We used the ‘profiles’ performance of the browser to begin each experiment in a contemporary surroundings, devoid from cookies, native storage and different applied sciences than preserve a state.
The browser, visiting the web site, was run on a pc related to the Web via an institutional community within the EU.
To create Shopper- and Server-side GTM installations, we created a brand new Google account, logged into it and adopted the instructed steps within the official GTM documentation.”
The outcomes of the evaluation comprise a number of crucial findings, together with that the “Google Tag” facilitates gathering a number of sorts of customers’ information with out consent and on the time of research it offered a safety vulnerability.
Information Assortment Is Hidden From Publishers
One other discovery was the extent of knowledge assortment by the “Pinterest Tag,” which garnered a big quantity of consumer information with out disclosing it to the Writer.
What some could discover disturbing is that publishers who deploy these tags could not solely be unaware of the info leaks however that the instruments they depend on to assist them monitor information assortment don’t notify them of those points.
The researchers documented their findings:
“We observe that the info despatched by the Pinterest Tag just isn’t seen to the Writer on the Pinterest web site, the place we logged in to watch Pinterest’s disclosure about collected information.
Furthermore, we discover that the info collected by the Google Tag about type interplay just isn’t proven within the Google Analytics dashboard.
This discovering demonstrates that for such Tags, Publishers should not conscious of the info collected by the Tags that they choose.”
Injections of Third Get together Scripts
Google Tag Managers has a characteristic for controlling tags, together with third get together tags, known as Net Containers. The tags can run inside a sandbox that limits their functionalities. The sandbox additionally makes use of a permission system with one permission known as inject_script that permits a script to obtain and run any (arbitrary) script exterior of the Net Container.
The inject_script permission permits the tag to bypass the GTM permission system to achieve entry to all browser APIs and DOM.
Screenshot Illustrating Script Injection
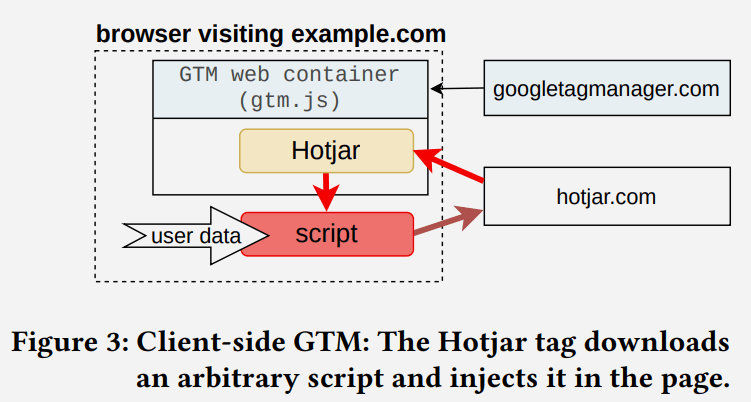
The researchers analyzed 78 formally supported Shopper-side tags and found 11 tags that don’t have the inject_script permission however can inject arbitrary scripts. Seven of these eleven tags have been supplied by Google.
They write:
“11 out of 78 official Shopper-side tags inject a third-party script into the DOM bypassing the GTM permission system; and GTM “Consent Mode” permits a few of the consent functions by default, even earlier than the consumer has interacted with the consent banner.”
The state of affairs is even worse as a result of it’s not only a privateness vulnerability, it’s additionally a safety vulnerability.
The analysis paper explains the that means of what they uncovered:
“This discovering reveals that the GTM permission system carried out within the Net Container sandbox permits Tags to insert arbitrary, uncontrolled scripts, thus opening potential safety and privateness vulnerabilities to the web site. Now we have disclosed this discovering to Google through their Bug Bounty on-line system.”
Consent Administration Platforms (CMP)
Consent Administration Platforms (CMP) are a expertise for managing what consent customers have granted when it comes to their privateness. It is a approach to handle advert personalization, consumer information storage, analytics information storage and so forth.
Google’s documentation for CMP utilization states that setting the consent mode defaults is the duty of the entrepreneurs and publishers who use the GTM.
The defaults might be set to disclaim advert personalizaton by default, for instance.
The documentation states:
“Set consent defaults
We suggest setting a default worth for every consent sort you might be utilizing.The consent state values on this article are solely examples. You might be accountable for ensuring that default consent mode is about for every of your measurement merchandise to match your group’s coverage.”
What the researchers found is that CMPs for Shopper-side GTMs are loaded in an undefined state on the webpage and that turns into problematic when a CMP doesn’t load default variables (known as undefined variables).
The issue is that GTM considers undefined variables to imply that customers have given their consent to the entire undefined variables, regardless that the consumer has not consented in any manner.
The researchers defined what’s occurring:
“Surprisingly, on this case, GTM considers all such undefined variables to be accepted by the tip consumer, regardless that the tip consumer has not interacted with the consent banner of the CMP but.
Amongst two CMPs examined (see §3.1.1), we detected this conduct for the Consentmanager CMP.
This CMP units a default worth to solely two consent variables – analytics_storage and ad_storage – leaving three GTM consent variables – security_-storage , personalization_storage functionality_storage – and consent variables particular to this CMP – e.g., cmp_purpose_c56 which corresponds to the “Social Media” goal – in undefined state.
These additional variables are therefore thought of granted by GTM. In consequence, all of the Tags that rely upon these 4 consent variables get executed even with out consumer consent.”
Authorized Implications
The analysis paper notes that United States privateness legal guidelines just like the European Union Common Information Safety Regulation (GDPR) and the ePrivacy Directive (ePD) regulate the processing of consumer information and using monitoring applied sciences and impose important fines for violations of these legal guidelines, akin to requiring consent for the storage of cookies and different monitoring applied sciences.
A authorized evaluation of the Shopper-Facet GTM flagged a complete of seven potential violations.
Seven Potential Violations Of Information Safety Legal guidelines
- Potential violation 1. CMP scanners usually miss functions
- Potential violation 2. Mapping CMP functions to GTM consent variables just isn’t compliant.
- Potential violation 3. GTM functions are restricted to clientside storage.
- Potential violation 4. GTM functions should not particular nor specific.
- Potential violation 5. Defaulting consent variables to “accepted” implies that Tags run with out consent.
- Potential violation 6. Google Tag sends information independently of consumer’s consent selections.
- Potential violation 7. GTM permits Tag Suppliers to inject scripts exposing finish customers to safety dangers.
Authorized evaluation of Server-Facet GTM
The researchers write that the findings increase authorized issues about GTM in its present state. They assert that the system introduces extra authorized challenges than resolutions, complicating compliance efforts and posing a problem for regulators to watch successfully.
These are a few of the components that brought about concern concerning the potential to adjust to laws:
- Complying with information topic rights is difficult for the Writer
For each Shopper- and Server-Facet GTM there is no such thing as a straightforward manner for a writer to adjust to a request for entry to collected information as required by Article 15 of the GDPR. The writer must manually monitor down each Information Collector to adjust to that authorized request. - Constructed-in consent raises belief points
When utilizing tags with built-in consent, publishers are compelled to belief that Tag Suppliers truly implement the built-in consent throughout the code. There’s no straightforward manner for a writer to assessment the code to confirm that the Tag Supplier is definitely ignoring the consent and gathering consumer info. Reviewing the code is not possible for official tags which are sandboxed throughout the gtm.js script. The researchers state that reviewing the code for compliance “requires heavy reverse engineering.” - Server-side GTM is invisible for regulatory monitoring and auditing
The researchers write that Server-side GTM blocks obstructs compliance auditing as a result of the info assortment happens remotely on a server. - Consent is difficult to configure on GTM Server Containers
Consent administration instruments are lacking in GTM Server Containers, which prevents CMPs from displaying the needs and the Information Collectors as required by laws.
Auditing is described as extremely troublesome:
“Furthermore, auditing and monitoring is solely attainable by solely contacting the Writer to grant entry to the configuration of the GTM Server Container.
Moreover, the Writer is ready to change the configuration of the GTM Server Container at any cut-off date (e.g., earlier than any regulatory investigation), masking any compliance verify.”
Conclusion: GTM Has Pitfalls And Flaws
The researchers have been gave GTM poor marks for safety and the non-compliant defaults, stating that it introduces extra authorized points than options whereas complicating the compliance with laws and making it arduous for regulators to watch for compliance.
Learn the analysis paper:
Google Tag Supervisor: Hidden Information Leaks and its Potential Violations underneath EU Information Safety Regulation
Obtain the PDF of the analysis paper right here.
Featured Picture by Shutterstock/Praneat

